Doctrine Of Ultra Vires

Beyond the powers is a latin phrase used in law to describe an act which requires legal authority but is done without it.
Doctrine of ultra vires. In this case the directors of the company i e ashbury railway carriage iron co. Section associated with the doctrine of ultra vires of the companies act is section 20 1 20 2 a b c and 20 3. Ltd entered into a contract with mr riche for providing finance for the construction of railway line in belgium. To apply the doctrine of ultra vires the first question for the courts to decide is whether the provision in the act prescribing the procedure is mandatory or directory.
The doctrine of ultra vires is a fundamental rule of company law. There are three types of ultra vires acts which. Doctrine of ultra vires has been developed to protect the investors and creditors of the company. Having seen the rational behind the ultra vires doctrine and the rules developed by courts to temper this doctrine it should be understood that there is always a thin line separating what is incidental or consequential to a certain power already granted and what is clearly ultra vires and as a result there is a lot of subjectivity involved in deciding what is ultra vires and what is not.
An ultra vires act is one beyond the purposes or powers of a corporation. It states that the objects of a company as specified in its memorandum of association can be departed from only to the extent permitted by the act. The earliest legal view was that such acts were void. Acts that are intra vires may equivalently be termed valid and those that are ultra vires termed invalid.
Its opposite an act done under proper authority is intra vires within the powers. Ultra vires doctrine in the companies act 1965. The doctrine of ultra vires played an important role in the development of corporate powers. Types of ultra vires acts.
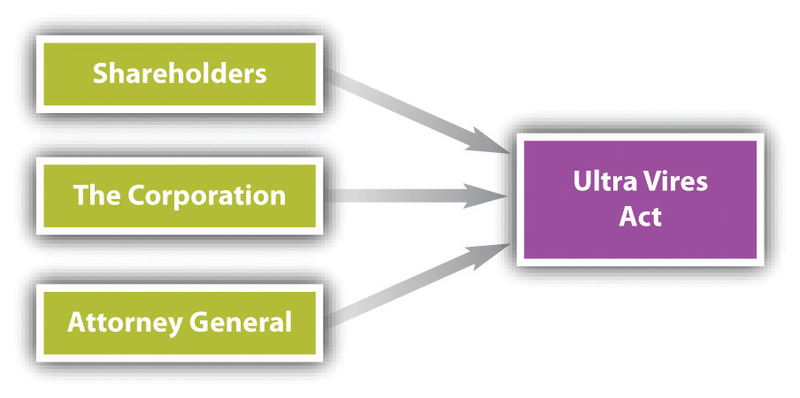
Under the companies act 1965 ca 1965 the ultra vires doctrine played a limited role in light of section 20 which provides that no act or purported act of a company and no conveyance or transfer of property to or by a company shall be invalid by reason only of the fact that the company was without capacity or power to do the act or to execute or take the conveyance or transfer. If the administrative authority fails to follow required procedure prescribed by parent act or by the general rule it is known as procedural ultra vires. The ultra vires doctrine is a kind of insurance policy that reassures a company s shareholders and creditors that the company will not use their assets or funds for any purposes other than those that are afforded to it and specified within the ultra vires doctrine. The doctrine of ultra vires however has its genesis in the english case of ashbury railway carriage and iron company ltd vs riche.